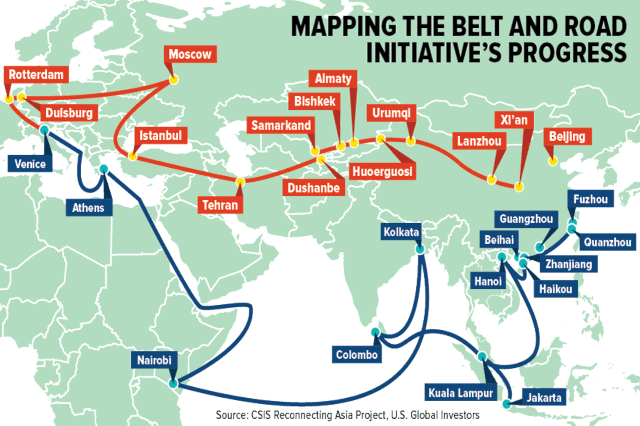
Introduction to The Belt and Road Initiative
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) , also known as the One Belt One Road (OBOR) initiative, is a massive infrastructure project launched by China in 2013. The initiative aims to connect Asia, Europe, and Africa through a network of railways, highways, ports, and other infrastructure projects, with the goal of promoting economic development, trade, and cultural exchange.
The Belt and Road Initiative consists of two main components: the Silk Road Economic Belt, which focuses on developing infrastructure and trade links across Central Asia and into Europe, and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, which aims to improve connections between China and countries in Southeast Asia, South Asia, and Africa.
Countries participated in the Belt and Road Initiative
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) involves a large number of countries that have either participated in BRI projects or signed treaties to support the initiative. Here is a list of some of the countries that have participated in the BRI or signed treaties related to the initiative:
Bangladesh, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Cambodia, China, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Ireland, Italy, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Mongolia, Montenegro, Myanmar, Nepal, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sweden, Switzerland, Tajikistan, Thailand, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, Uzbekistan, Vietnam.
As the BRI is a large-scale and ongoing initiative, and the list of participating countries is subject to change over time as new projects are launched and new countries become involved.
As of now, the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has made significant progress since its launch in 2013. According to the Chinese government, as of 2021, over 140 countries and international organizations have signed BRI cooperation agreements, and China has invested over US$4 trillion in BRI projects.
Some of the key achievements of the BRI include:
- Infrastructure Development:
The BRI has supported the construction of various infrastructure projects, including railways, highways, ports, and airports, in participating countries. These projects have helped to improve connectivity and promote economic development in these regions.
- Trade and Investment:
The BRI has also facilitated increased trade and investment between China and participating countries. According to the Chinese Ministry of Commerce, trade between China and BRI countries reached US$9.2 trillion between 2013 and 2020.
- People-to-People Exchanges:
The BRI has also promoted cultural and people-to-people exchanges between China and participating countries through initiatives such as educational and cultural exchanges, tourism, and academic research cooperation.
However, the BRI has also faced criticism and challenges.
Concerns on BRI are :
- Debt Sustainability:
Many of the countries involved in the Belt and Road Initiative are developing economies with limited resources. Critics worry that the large-scale infrastructure projects could lead to unsustainable debt burdens for these countries.
- Environmental Impacts:
The Belt and Road Initiative involves massive infrastructure projects that could have significant environmental impacts, including deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution.
- Lack of Transparency:
Critics have also raised concerns about the lack of transparency surrounding Belt and Road projects. Some worry that the initiative could be used to promote China’s geopolitical agenda, rather than benefiting the countries involved.
- Potential geopolitical implications of China’s growing influence.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has also impacted BRI projects, causing delays and disruptions in some cases. Despite these challenges, China remains committed to the BRI, and the initiative continues to move forward with new projects and partnerships.
Success stories on BRI :
However, the participating countries have seen success on how the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has uplifted countries in social and economic terms through better infrastructure. Here are a few examples.
PAKISTAN
The BRI has helped to upgrade Pakistan’s infrastructure, including the construction of the Gwadar Port in Balochistan, which has created new economic opportunities and improved connectivity between Pakistan and other countries. Additionally, the BRI has helped to build new highways and railways in Pakistan, improving transportation and trade links between the country and its neighbors.
ETHOPIA
The BRI has supported the construction of the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway, which has improved trade links between Ethiopia and Djibouti and enhanced economic growth in the region. The railway has also created jobs and opportunities for local communities, including the training of local technicians and engineers to operate and maintain the railway.
MALAYSIA
The BRI has supported the construction of the East Coast Rail Link (ECRL), which is expected to connect the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia to major ports and industrial areas in the west. The ECRL is expected to create new economic opportunities and promote regional development in Malaysia, including the development of new industries and the creation of new jobs.
SERBIA
The BRI has supported the construction of the Belgrade-Budapest railway, which will connect Serbia with Hungary and the rest of Europe. The project is expected to improve transportation links, promote economic development, and enhance regional connectivity in the Balkans.
GREECE
The BRI has supported the construction of the Piraeus Port in Greece, which has become one of the largest ports in Europe and has helped to increase trade links between China and Europe. The port has also created new economic opportunities and jobs for local communities.
ITALY
The BRI has supported the development of the Port of Trieste, which is a key hub for trade between China and Europe. The port has helped to increase trade links and has created new economic opportunities for the region.
PORTUGAL
The BRI has supported the construction of the Sines Port in Portugal, which has become a key hub for trade between China and Europe. The port has created new economic opportunities and jobs for the region, and has helped to enhance connectivity between Portugal and other European countries.
KAZAKHSTAN
The BRI has supported the construction of the Khorgos Gateway, a major logistics hub on the border between Kazakhstan and China. The hub has helped to improve connectivity and trade links between the two countries, and has created new economic opportunities for local communities through the development of new businesses and industries.
In conclusion
The Belt and Road Initiative is a massive infrastructure project that aims to connect Asia, Europe, and Africa through a network of railways, highways, ports, and other infrastructure projects. By improving connectivity, creating new economic opportunities, and enhancing regional development, the BRI has helped to promote economic growth and social progress in participating countries.
While the initiative has the potential to bring significant economic benefits to the countries involved, there are also concerns need to be addressed too.
As the Belt and Road Initiative continues to develop, it will be important to address these issues and ensure that the projects are sustainable, transparent, and respectful of the environment and local communities. By doing so, the Belt and Road Initiative could help to promote economic development and cultural exchange, while also building stronger relationships between countries.